1. (2 pts) Which chemical group is at the 5’ end of a single polynucleotide strand?
A. Hydroxyl group
B. Phosphate group
C. Diester group
D. Purine base
E. Nitrogen group
Answers seen: A (0), B (63), C (0), D (0), E (0)
2. (2 pts) Which chemical group is at the 3’ end of a single polynucleotide strand?
A. Phosphate group
B. Hydroxyl group
C. Purine group
D. Nitrogen group
E. Methyl group
Answers seen: A (0), B (59), C (0), D (3), E (1)
3. (2 pts) If guanine makes up 23% of the nucleotides in a sample of double-stranded DNA then thymine would make up what percent of the bases?
A. 23%
B. 30%
C. 46%
D. 27%
E. 15%
Answers seen: A (5), B (0), C (0), D (58), E (0)
Explanation: If G is 23%, then C is 23%, so GC = 46%. This means that AT must be 54%, so T is 27%.
4. (2 pts) Which of the following is not true regarding the structure of DNA?
A. Each chain makes one complete turn every 34 angstroms
B. The two strands are antiparallel
C. Ionic bonds are the main force holding the strands together
D. The purine adenine base pairs with the pyrimidine thymine
E. The paired bases are parallel to one another and perpendicular to the long axis of the helix
Answers seen: A (0), B (2), C (58), D (1), E (2)
Explanation: Hydrogen bonds hold the strands together.
5. (2 pts) Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a DNA strand in the 5’ – 3’ direction?
A. Primase
B. Ligase
C. DNA polymerase
D. Topoisomerase
E. Helicase
Answers seen: A (11), B (2), C (48), D (1), E (1)
6. (2 pts) The enzyme activity of DNA polymerase that functions in proofreading is
A. 5’ to 3’ exonuclease
B. 3’ to 5’ exonuclease
C. Glycosylase
D. DNA ligase
E. Flap endonuclease
Answers seen: A (19), B (43), C (0), D (1), E (0)
7. (2 pts) DNA ligase functions to
A. Catalyze the formation of hydrogen bonds between adjacent 5’-P and 3’-OH termini
B. Relax supercoiling of DNA
C. Add methyl groups to DNA
D. Facilitate base pairing between single-stranded molecules of DNA
E. Catalyze the formation of covalent bonds between adjacent 5’-P and 3’-OH termini
Answers seen: A (11), B (3), C (0), D (6), E (43)
8. (2 pts) Discontinuous replication means that
A. DNA synthesis begins at multiple origins of replication
B. DNA synthesis starts and stops many times before being completed
C. DNA synthesis is not continuous with RNA synthesis
D. One of the daughter strands of a replicated piece of DNA is made in short fragments that are joined together
Answers seen: A (3), B (5), C (1), D (54)
9. (2 pts) The leading strand is
A. The single DNA strand that is synthesized as a continuous unit
B. A single DNA strand synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately joined together
C. Single-stranded RNA primers used in DNA synthesis
D. The template strand from which the new strand is synthesized
E. None of the above
Answers seen: A (58), B (0), C (0), D (4), E (1)
10. (2 pts) Which of the following statements about PCR is false?
A. PCR stands for polymerase chain reaction
B. PCR uses short oligonucleotide primers
C. PCR uses a DNA polymerase to synthesize DNA
D. PCR can be used to obtain large quantities of a particular DNA sequence
E. PCR does not require knowledge of the DNA sequences at the ends of the region to be amplified
Answers seen: A (2), B (18), C (8), D (1), E (33)
Explanation: We need to know the sequence at the ends of the region to be amplified in order to make the primers. Please see the study guide.
11. (2 pts) If mature eukaryotic mRNA is hybridized with its corresponding DNA coding strand (heteroduplex analysis) and visualized by electron microscopy, looping strands of nucleic acid are seen. What do these structures represent?
A. Lariat structures
B. tRNAs
C. Introns
D. Exons
E. Overlapping genes
Answers seen: A (6), B (7), C (38), D (6), E (6)
Explanation: Please see the lecture notes.
12. (2 pts) In eukaryotes, the primary transcript is
A. The most abundant mRNA from a particular gene derived from alternative splicing
B. The RNA molecule that is a direct copy of a segment of the genome, prior to RNA processing
C. The most abundant mRNA in the cell
D. The zygotic mRNA expressed first following fertilization
E. The longest mRNA from a particular gene
Answers seen: A (12), B (43), C (6), D (1), E (1)
Explanation: Please see the lecture notes.
13. (2 pts) Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription?
A. Nucleotides are added to the 5’ end of the newly synthesized strand
B. A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3’ hydroxyl and the 5’ phosphate
C. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence
D. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming
E. Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequences
Answers seen: A (8), B (26), C (1), D (5), E (23)
14. (2 pts) The four ribonucleotide triphosphates incorporated into mRNA are
A. Inosine, Guanine, Uracil, Thymine
B. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
C. Cytosine, Uracil, Adenine, Guanine
D. Thymine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
E. Inosine, Guanine, Adenine, Cytosine
Answers seen: A (0), B (0), C (61), D (2), E (0)
15. (2 pts) Which of the following statements is true regarding gene expression?
A. The 3’ end of the mRNA corresponds to the carboxyl terminus of the protein.
B. The first step is the association of mRNA with ribosomes
C. Involves proofreading of the mRNA
D. Prokaryotic RNA usually undergoes nuclear processing
E. Polypeptides are synthesized by addition of amino acids to the amino terminus
Answers seen: A (22), B (15), C (6), D (2), E (19)
Explanation: B. The first step of gene expression is transcription.
C. There is proofreading in DNA synthesis, but not in transcription or translation.
D. Prokaryotes don't have nuclei, and don't process RNA after transscription.
E. Polypeptides are synthesized by addition of amino acids to the carboxyl terminus.
16. (2 pts) To describe the genetic code as degenerate indicates that
A. mRNA is rapidly degraded
B. The code is not universal among organisms
C. Some amino acids have more than one codon
D. Frameshift mutations are tolerated
E. Stop codons may have corresponding tRNA molecules
Answers seen: A (4), B (3), C (50), D (3), E (3)
17. (2 pts) Which of the following statements is true?
A. tRNAs are charged by binding to the ribosome
B. The anticodon of one tRNA can bind with several different codons
C. There are more distinct tRNAs than codons
D. Amino acids are bound to the 5’ end of charged tRNAs
E. tRNA has a 5’ triphosphate
Answers seen: A (13), B (20), C (6), D (15), E (9)
Explanation: A. tRNAs are charged by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (charging enzymes).
C. There are more codons than distinct tRNAs (wobble).
D. Amino acids are bound to the 3' end of charged tRNAs.
E. tRNA, like other RNAs, has a 5' phosphate.
18. (2 pts) Which of the following statements about translation is correct?
A. Translation termination occurs when the ribosome reaches the 3’ end of the mRNA.
B. In translation initiation, an aminoacyl tRNA binds the start codon on the mRNA before the large ribosomal subunit binds.
C. In bacterial translation initiation, sigma factor recruits the large ribosomal subunit.
D. Peptide bonds are synthesized between a polypeptide chain attached to the large ribosomal subunit and an aminoacyl tRNA in the E site.
E. Translation termination occurs when an uncharged tRNA recognizes the stop codon in the A site.
Answers seen: A (1), B (23), C (6), D (4), E (28)
Explanation: A. Translation termination occurs when a stop codon is reached.
C. Sigma factor is a bacterial transcription initiation factor.
D. Peptide bonds are synthesized between a polypeptide chain that had been attached to a tRNA and an aminoacyl tRNA in the A site.
E. Translation termination occurs when a release factor recognizes the stop codon in the A site.
19. (2 pts) Which of the following statements about mutations is correct?
A. In a nonsense mutation, multiple amino acids are added to the carboxyl terminus compared to the wild-type protein sequence.
B. In a missense mutation, the stop codon is changed to a codon for an amino acid.
C. In a silent mutation, transcription of the gene is silenced.
D. In a splice site mutation, multiple amino acids may be missing from the protein product.
E. In a frameshift mutation, deletion or addition of three bases causes a single amino acid to be gained or lost.
Answers seen: A (2), B (2), C (4), D (38), E (17)
Explanation: Please see the lecture notes.
20. (2 pts) Which of the following statements about forensic analysis of short terminal repeats (STRs) is false?
A. Saliva from a cigarette butt, licked envelope, or chewing gum contains enough human DNA to conduct forensic analysis.
B. Short terminal repeats consist of a variable number of repeats of a short DNA sequence flanked by unique sequence.
C. Primers that recognize the unique sequence flanking STRs are used to amplify DNA using PCR.
D. Amplified DNA is analyzed by mass spectrometry.
E. The probability of two unrelated people sharing a DNA profile derived from the analysis of 14 standard markers is about one in a billion.
Answers seen: A (8), B (13), C (8), D (31), E (3)
Explanation: Please see the lecture notes.
21. (5 pts) What would happen if DNA synthesis were discontinuous on both strands?
A. The DNA fragments from the two new strands could become mixed, producing mutations.
B. DNA synthesis would not occur because the appropriate enzymes to carry out discontinuous replication on both strands would not be present.
C. DNA synthesis might take longer, but otherwise there would be no noticeable difference.
D. DNA synthesis would not occur, as the entire length of the chromosome would have to be unwound before both strands could be replicated in a discontinuous fashion.
Answers seen: A (5), B (17), C (19), D (22)
22. (5 pts) Which of the following is true about eukaryotic mRNA?
A. Sigma factor is essential for correct initiation of transcription.
B. Processing of the nascent mRNA may begin before its transcription is complete.
C. Processing occurs in the cytoplasm.
D. Termination occurs via a hairpin loop or use of rho factor.
E. Many RNAs can be transcribed simultaneously from one DNA template.
Answers seen: A (6), B (3), C (25), D (14), E (15)
Explanation: A. Sigma factor is essential for correct initiation of transcription in prokaryotes.
B. Polyadenylation of the 3' end cannot possibly begin before transcription is complete.
C. Processing occurs in the nucleus.
D. Termination occurs via a hairpin loop or use of rho factor in prokaryotes.
23. (5 pts) Archibald Garrod described people with alkaptonuria, whose urine turns black upon exposure to air due to the presence of an aromatic compound, homogentisic acid. There is more homogentisic acid in the urine of alkaptonurics after a heavy protein meal. Pure phenylalanine and tyrosine cause an increase in the output of homogentisic acid in the urine when fed to people with alkaptonuria, but pure tryptophan does not. The best explanation for these results is
A. Tryptophan is excreted unchanged in the urine of people with alkaptonuria.
B. Phenylalanine and tyrosine share a common degradative pathway that has homogentisic acid as an intermediate.
C. People with alkaptonuria have a defect in the urea cycle.
D. People with alkaptonuria cannot convert phenylalanine to tyrosine.
E. People with alkaptonuria have an inherited disorder in the enzyme that converts tryptophan to homogentisic acid.
Answers seen: A (2), B (49), C (3), D (3), E (7)
Explanation: Please see the lecture notes.
24. Yeast is a single-celled fungus capable of growing on synthetic minimal medium containing only inorganic salts, a nitrogen source, and a carbon source such as glucose. A collection of mutant yeast strains is isolated that requires compound G for growth. The compounds (A to E) in the biosynthetic pathway to G are known, but their order in the pathway is not known. Each compound is tested for its ability to support the growth of each mutant (1 through 5). In the table below, a plus sign indicates growth and a minus sign indicates no growth.
| Compound tested | ||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | G | |
| mutant 1 | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| mutant 2 | - | + | - | + | - | + |
| mutant 3 | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| mutant 4 | - | + | + | + | - | + |
| mutant 5 | + | + | + | + | - | + |
a. (5 pts) What is the order of compounds A to E in the pathway?
A. E → C → D → A → B → G
B. D → B → C → A → E → G
C. E → A → C → B → D → G
D. A → B → C → D → E → G
E. There is not enough information to solve the problem.
Answers seen: A (0), B (4), C (58), D (0), E (0)
Explanation: It is easier to solve this if we rearrange the table. First, let's change the order of the columns as shown below. We have arranged the columns so that the compound that supports the growth of the most strains (G) is on the right. The compound that supports the growth of the fewest strains (E) is on the left.
| Compound tested | ||||||
| E | A | C | B | D | G | |
| mutant 1 | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| mutant 2 | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| mutant 3 | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| mutant 4 | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| mutant 5 | - | + | + | + | + | + |
Then, let's change the order of the rows as shown below. We have rearranged the rows so that the strain that grows on the most compounds (mutant 5) is at the top. The strain that grows on the fewest compounds (mutant 3) is at the bottom.
| Compound tested | ||||||
| E | A | C | B | D | G | |
| mutant 5 | - | + | + | + | + | + |
| mutant 4 | - | - | + | + | + | + |
| mutant 2 | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| mutant 1 | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| mutant 3 | - | - | - | - | - | + |
We can see that the strain that grows on the fewest compounds (only the end product) is mutant 3. This must be blocked in the last step of the pathway. The strain that grows on the most compounds is mutant 5, which must be blocked early in the pathway. When we rearrange the table this way, it is clear that the order of the compounds in the pathway is:
E → A → C → B → D → G
b. (5 pts) At what point in the pathway is mutant 4 blocked?
A. The conversion of E to G
B. The biosynthesis of E
C. The conversion of A to C
D. The conversion of A to E
E. There is not enough information to solve the problem.
Answers seen: A (5), B (2), C (41), D (9), E (7)
Explanation: Mutant 4 grows on C, B, D, and G, so it must be blocked in the conversion of A to C.

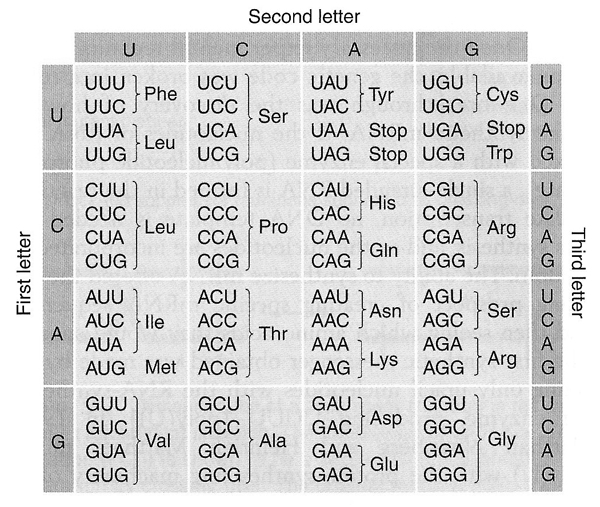
25a. (6 pts) Use the codon table above to complete the table below. Assume that reading is from left to right and that the columns represent an alignment of transcription and translation.
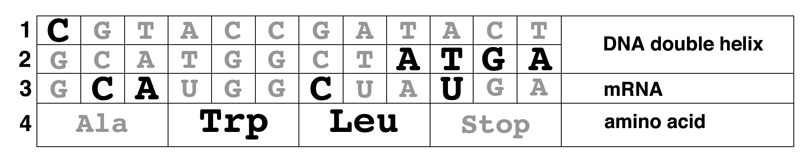
Explanation: Original text shown in black, answers in gray.
First we check to see if the mRNA is written from left to right with the 5' end at the left. The key is the leucine codon. We can see that if the mRNA is written from left to right, the leucine codon starts with C and ends with A. We know that the leucine codon ends with A because there is an A in the bottom DNA strand at position 9, and the T for U at position 10 tells us that the bottom DNA strand of DNA is the mRNA written as DNA; the top strand of the DNA is the template. CXA is the leucine codon CUA. If the mRNA is written from right to left, the codon here is AXC, which cannot be a leucine codon. The leucine codons are UUA, UUG, and CUX.
This tells us that mRNA positions 7-9 are CUA. We know that the bottom DNA strand written as RNA is the mRNA sequence, so the codon at mRNA positions 10-12 is UGA, a stop codon. Tryptophan is the unique codon UGG, so we know that the codon at mRNA positions 4-6 is UGG. The DNA base in position 1 one on the complementary strand is C, so we know that the DNA base in position 1 on the bottom strand and in the mRNA is G, so the codon at mRNA positions 1-3 is GCA. GCA is an alanine codon. Now that we have the complete sequence of the mRNA, we can complete the DNA sequence.
Please see the study guide.
Grading: entirely correct answers get points, no partial credit. Line 1 correct 1 pt; line 2 correct 1 pt, line 3 correct 2 pts; line 4 correct 2 pts. "Stop" is shown as answer for last aa; none, end, other synonyms OK.
Answers seen: 6 pts (36), 5 pts (8), 4 pts (1), 3 pts (1), 2 pts (4), 1 pt (0), 0 pts (15)
25b. (2 pts) The leftmost position of line 1 represents:
A. The 5’ end
B. The 3’ end
C. The amino terminus
D. The carboxyl terminus
E. There is not enough information to solve the problem.
Answers seen: A (30), B (32), C (0), D (1), E (0)
25c. (2 pts) The leftmost position of line 4 represents:
A. The 5’ end
B. The 3’ end
C. The amino terminus
D. The carboxyl terminus
E. There is not enough information to solve the problem.
Answers seen: A (7), B (4), C (43), D (5), E (0)

Use the codon table above to answer the questions below.
26. (5 pts) How many synonymous changes can be made by single base-pair substitution starting with the codon CGG?
A. None
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
E. Six
Answers seen: A (0), B (4), C (26), D (29), E (4)
Explanation: Starting with CGG (Arg), we can generate nine codons by single base-pair substitutions, shown with the amino acids that they encode below. Synonymous substitutions are highlighted in yellow.
| AGG | Arg |
| TGG | Trp |
| GGG | Gly |
| CAG | Gln |
| CCG | Pro |
| CTG | Leu |
| CGA | Arg |
| CGC | Arg |
| CGT | Arg |
Four of the nine codons derived from CGG by single-base substitutions are synonymous. Please see the study guide.
27. (5 pts) How many different codons can be generated by single-base transversions starting with the codon CGG?
A. Two
B. Four
C. Six
D. Eight
E. Sixteen
Answers seen: A (1), B (8), C (35), D (17), E (2)
Explanation: There are six codons that can be derived from CGG by single-base transversions, shown below.
| AGG |
| GGG |
| CCG |
| CTG |
| CGC |
| CGT |
Please see the study guide.
28. (5 pts) What fraction of the codons generated by single-base transversions starting with the codon CGG are synonymous?
A. None
B. 1 / 4
C. 1 / 3
D. 1 / 2
E. 3 / 4
Answers seen: A (1), B (13), C (15), D (30), E (4)
Explanation: Three of the six codons (1/2) generated by single-base transversions starting with CGG (Arg) are synonymous, highlighted in yellow below.
| AGG | Arg |
| GGG | Gly |
| CCG | Pro |
| CTG | Leu |
| CGC | Arg |
| CGT | Arg |
Please see the study guide.
29. (5 pts) Which of the following describes an experimental strategy used to establish the semiconservative replication of DNA?
A. analysis of mutants defective in DNA synthesis
B. study of human patients with defects in DNA repair
C. density gradient centrifugation of bacterial DNA sampled at different times after a shift from density-labeled medium to light medium
D. sucrose gradient centrifugation of bacterial DNA sampled at different times after a shift from normal medium to medium containing 32P
Answers seen: A (1), B (1), C (41), D (20)
Explanation: This is the Meselson-Stahl experiment. Please see the lecture notes.
30. (5 pts) Which of the following describes an experimental strategy used to decipher the genetic code?
A. comparing the amino acid sequence of proteins to the nucleotide sequence of their genes in humans
B. analyzing the sequence of RNAs produced from known DNA sequences
C. analyzing mutants that changed the code
D. examining the polypeptides produced when RNAs of known sequence were translated
Answers seen: A (16), B (13), C (9), D (25)
Explanation: This is the approach first used by Nirenberg. Please see the lecture notes.